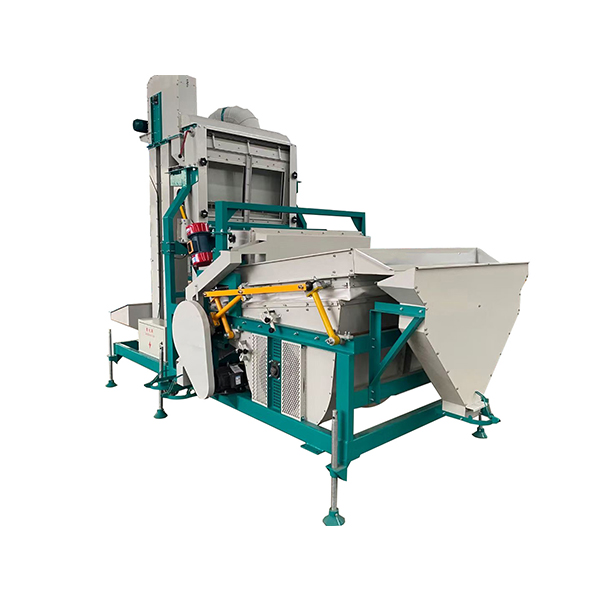
The air-screen gravity separator is a composite material cleaning device that integrates air separation and screening processes with gravity separation as its core process. It is the mainstream equipment for impurity removal and grading of granular materials such as beans, grains, and oilseeds. It can remove impurities of different sizes, weights, and particle sizes with different specific gravities in a single pass, with a cleaning accuracy far exceeding that of a single air-screen separator. It is primarily suitable for granular materials such as soybeans, chickpeas, peas, sesame, corn, and wheat, and is widely used in agricultural product processing, grain storage, and seed selection.
The key to cleaning impurities in beans using an air-screen gravity separator is to accurately match equipment parameters according to the bean variety and impurity type, control the feeding and operating status, and perform proper pre-treatment and post-maintenance. It is crucial to ensure cleaning accuracy while avoiding bean damage and equipment malfunction. Different beans (soybeans, chickpeas, peas, kidney beans, etc.) have different particle sizes, specific gravities, and skin characteristics, requiring specific adjustments to operating precautions.
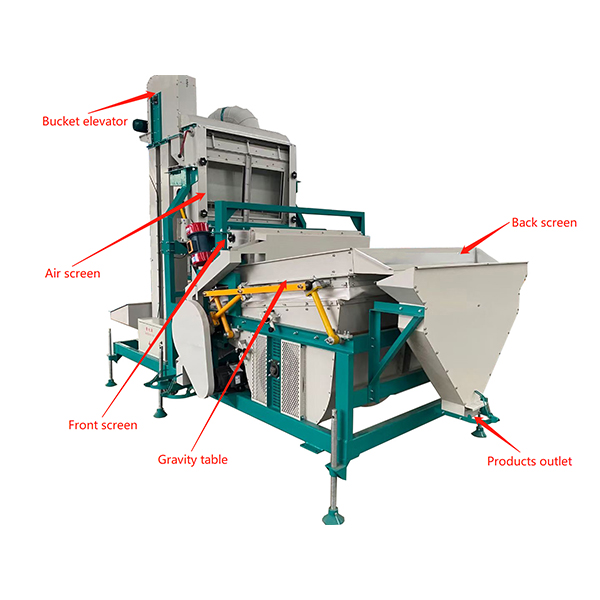
Core Structure: Three Core Systems + Auxiliary Supports, Modular Design
The equipment is an integrated frame with modular connections between each process. Material enters through the inlet and undergoes three cleaning stages sequentially without additional transfers. The core structure consists of a feeding system, a core cleaning system, and a discharge system, plus auxiliary systems such as electrical control and lubrication. Each component’s function is precisely matched to the cleaning requirements:
Feeding System: Includes a feed hopper, speed-regulating guide plate, and equalizing roller. Its core function is to provide stable, uniform, and thin-layer feeding, controlling the feed rate and material distribution to avoid one-sided accumulation and ensure the processing effect of subsequent cleaning stages. The speed-regulating guide plate can adjust the feeding speed according to material characteristics and equipment throughput;
Core Cleaning System (Core Process) The core of the equipment consists of three interconnected processes. Materials pass through the following stages sequentially:
Pre-screening section: This section initially screens for large impurities (straw, large weed seeds) and coarse impurities (sand, broken particles), reducing the load on subsequent processes. It typically uses a single-layer round-hole screen.
Air separation zone: This zone includes a centrifugal fan, air duct, and air guide plates. It separates light impurities (bean husks, shriveled shells, light weed seeds) through directional airflow. The airflow path is adjustable and the air volume is infinitely variable.
Main screening section:This section precisely grades impurities by size. It typically uses a double-layer round-hole screen (the upper screen catches large impurities, the lower screen catches small impurities). The screens can be quickly disassembled and replaced to accommodate materials of different particle sizes.
Gravity separation section:his section includes a gravity table, vibrating motor, and bottom fan. The gravity table is corrugated. The screen features a raised, non-slip surface and a bottom fan providing uniform upward airflow. A vibrating motor drives the gravity table to reciprocate, which is crucial for removing impurities of the same particle size but different specific gravities.
The discharge system includes a qualified material receiving hopper and collection ports for large/small/light/heavy impurities. Each discharge port is independent to prevent impurities from mixing back into the material. The collection ports can be connected to a silo or conveyor belt for continuous production.
The auxiliary system includes an electrical control cabinet (for centralized control of the motor, speed regulation, and start/stop), bearing/transmission lubrication points, and a dust cover. Some high-end models include frequency conversion speed regulation and impurity level alarm functions.
I. Pre-treatment before cleaning: Reduce equipment load and avoid jamming/damage. First, perform manual initial cleaning to remove large, hard impurities (stones, metal shavings, wood blocks, hard plastic pieces, straw bundles) mixed in with the beans. These impurities can clog the screen, wear down the gravity table screen surface, and even damage the equipment’s transmission components. Metal impurities can also cause sparks, posing a safety hazard.
II. Screening process adjustment: Match the particle size difference between beans and impurities, focusing on preventing clogging and leakage.
III. Air separation process adjustment: Match the specific gravity difference between beans and impurities, focusing on preventing blowaway and residual impurities. The air separation process mainly removes light impurities (bean husks, straw, shriveled shells, light weed seeds). By controlling the airflow of the blower, light impurities are separated from the material flow and must be coordinated with the screening process.
IV. Specific Gravity Process Adjustment: Removes impurities of the same particle size but different specific gravities, preventing core stratification failure.
Specific Gravity Table Screen Surface Selection: Use a corrugated/pricked anti-slip screen surface (to prevent beans from slipping during vibration and ensure stratification). The screen aperture should be slightly smaller than the qualified bean size, allowing airflow to pass through the screen holes without allowing beans to leak out.
V. Equipment Operation: Real-time monitoring for stable operation and fault prevention.
No-load Trial Run: Before each startup, run the machine under no-load for 3-5 minutes. For 1 minute, check the operating status of the blower, motor, transmission components, and gravity table to ensure there are no abnormal noises or jams, and that the screen and air duct are well sealed. Feed material only after the equipment is running stably; do not start the machine with material on (this can easily lead to blockage at the feed inlet and motor overload).
VI. Equipment Maintenance and Cleaning: Extending lifespan and ensuring stable cleaning accuracy
Clean after each use: Use a soft brush to clean the screen, gravity table surface, air duct, and material inlet to remove accumulated debris (sand, bean skins, shriveled beans) to prevent hardening and adhesion, which can affect the screening and air separation effect in the next use. Use compressed air to blow away dust from the dead corners inside the equipment. Do not directly wash the motor, electrical control box, bearings, etc. with water to prevent short circuits and rust.
Post time: Jan-27-2026